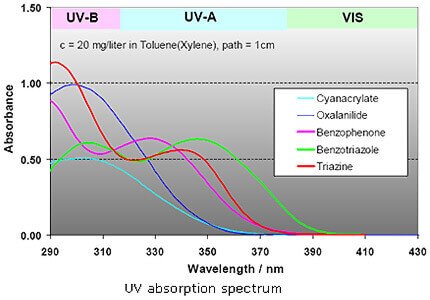
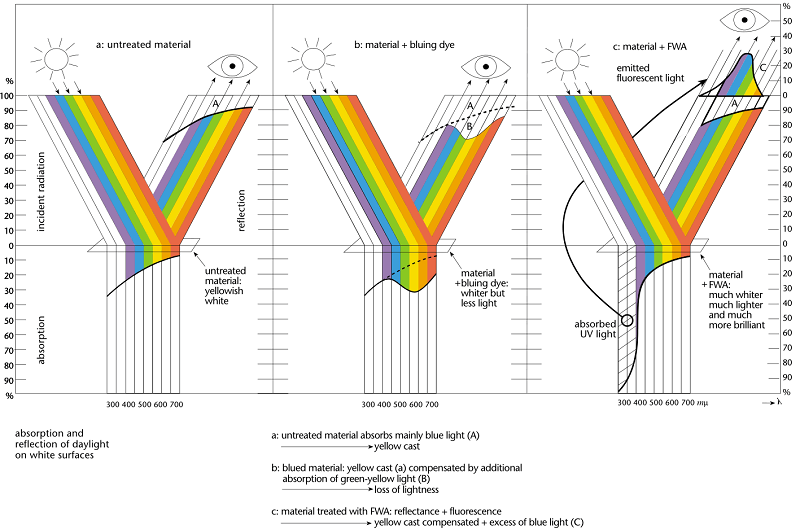
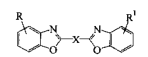
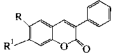
- UV Absorber & Light Stabilizers Market
- UV Absorber & Light Stabilizers Trend
1. UV Absorber & Light Stabilizers Market
In year 2015, global plastic and coating uv absorber (include light stabilizers) market scale is about 13 Billion RMB,and with 3% to 4% compound average growth rate(CAGR) in next four years. This attributes to industrial development in emerging market plus significant growth in demand for coating globally.For example, automotive and industrial paint has driven the demand for polymer additives. With threshold of high techniques in additives manufacturing and developing, uv absorbers (include light stabilizers) manufacturers was located in few chemistry-developed countries.Opportunities of growth exists in new market and exploring in new applications.
2. UV Absorber & Light Stabilizers Trend
to be updated...